 井字棋棋盘
井字棋棋盘
Tic-Tac-Toe又称井字棋,即在3X3的棋盘上,双方轮流落子,先将3枚棋子连成一线的一方获得胜利。
Tic-Tac-Toe变化简单,只有765个可能局面,26830个棋局,因此常成为博弈论和游戏树搜寻的教学例子,同时也是人工智能的一道好题目。
关于棋盘:
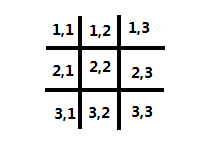 井字棋棋盘坐标版
井字棋棋盘坐标版
整个棋盘可以连接出8条线。tic-tac-toe 井字棋 胜利方式(如右图)——>
在中心的位置(2,2)有四条线穿过。
在所有棱位(1,2),(2,1),(2,3),(3,2),均有两条线穿过。
在所有角位(1,1),(1,3),(3,1),(3,3),均有三条线。
如何实现人工智能:
在下棋过程中,任何一方无非处于四种状态:
开局落子
第二步棋(先角原则)
攻
守
垃圾时间
想要实现人工智能,让AI和人正常对弈,必须让AI理解这5种状态。
开局落子:
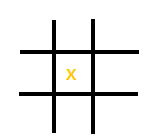 井字棋 AI先手[/caption]
井字棋 AI先手[/caption]
开局时,分为两种状况,一是AI先手,二是AI后手。AI先手时,毫无疑问,让AI落子在(2,2)位置(以X表示AI)。如图:
而当AI后手时,玩家可能落子情况有分为三种:
中心位置
棱位
角位
1、玩家落子在中心位置:
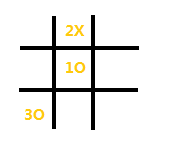 图1[/caption]
图1[/caption]
此时,AI需要落子在角位。原因在于,如果落子在棱位,将出现如下必输的情形,示例如下,AI此时落子在(1,2)位置:玩家只需要在(3,1)或(3,3)位置落子,如图在(3,1),下一步则必须落子在(1,3),对手跟进落子在(1,1),
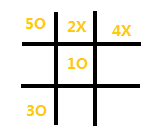 ——则AI大势已去!
——则AI大势已去!
2、棱位 3、角位
这两种情形,AI指需要落子在(2,2)位置,便可保无虞,甚至反守为攻。
第二步棋(先角原则):
 由上可知,当中心被玩家占据,需要避免上边提到的“必输的情形”跟进落子在角上,而非棱上。
由上可知,当中心被玩家占据,需要避免上边提到的“必输的情形”跟进落子在角上,而非棱上。
而如果,自己占据中心,玩家落子在棱上,根据“必输情形”,此时也应该落在角上,而且如上图图1,应该落子在玩家棋子对面的角位上,此时“必输情形”将属于玩家。
攻:
任何己方两枚棋子连接在一起,且连线有空位时,落子在空位。
守:
任何玩家两枚棋子连接在一起,且连线有空位时,落子在空位。
垃圾时间:
由于棋盘大小限制,下棋过程中,很容易陷入双方均无法获胜的情况,此时,只需要找个空位随便落子即可。
特殊情况:
在以以上方式实现AI时,出现了一种比较特殊情况。即玩家先手,落子在角位以(1,1)为例,AI根据“开局落子”的原则3,落子在(2,2)。而玩家在第一步棋子位置(1,1)的对角(3,3)位置落子,
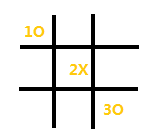 井字棋 特殊情况[/caption]
井字棋 特殊情况[/caption]
依据“角先原则”,AI将落子在(1,3)或(3,1),对方将在(3,1)或(1,3)封堵AI,此时AI便已输了。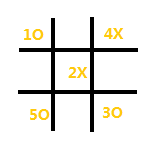
所以,唯有此种情况不能执行“角先原则”。
代码实现:
其中,以二维数组t[3][3]表示棋盘,-1表示AI棋子X,1表示玩家棋子O,
dropPiece(Position p)方法表示落子,Position(int f ,int x,int y)表示棋盘位置,x,y表示坐标值,f取值范围为(-1或1)表示AI或者玩家。下面是AI类主要代码:
public void start(){
if(attrack()){//实现攻
}else if(defend()){//实现守
}else if(center()){//实现开局落子
}else{
planB();//实现特殊情况、先角原则及垃圾时间
}
}//以上方法是AI运行开始的方法
public boolean attrack(){
return twoPieces(-1);
}//攻,任何己方两枚棋子连接在一起,且连线有空位时,落子在空位。
public boolean defend(){
return twoPieces(1);
}//守,任何对方两枚棋子连接在一起,且连线有空位时,落子在空位。
private boolean twoPieces(int f) {
for(int i=0;i<=t.length-1;i++){
if(t[i][0]==t[i][1]&&t[i][0]==f&&t[i][2]==0){
b.dropPiece(new PieceLocation(-1,i,2));return true;
}else if(t[i][0]==t[i][2]&&t[i][0]==f&&t[i][1]==0){
b.dropPiece(new PieceLocation(-1,i,1));return true;
}else if (t[i][1]==t[i][2]&&t[i][1]==f&&t[i][0]==0){
b.dropPiece(new PieceLocation(-1,i,0));return true;
}else if(t[0][i]==t[1][i]&&t[0][i]==f&&t[2][i]==0){
b.dropPiece(new PieceLocation(-1,2,i));return true;
}else if (t[0][i]==t[2][i]&&t[0][i]==f&&t[1][i]==0){
b.dropPiece(new PieceLocation(-1,1,i));return true;
}else if(t[1][i]==t[2][i]&&t[1][i]==f&&t[0][i]==0){
b.dropPiece(new PieceLocation(-1,0,i));return true;
}
}
if (t[0][0]==t[1][1]&&t[0][0]==f&&t[2][2]==0){
b.dropPiece(new PieceLocation(-1,2,2));return true;
}else if(t[1][1]==t[2][2]&&t[1][1]==f&&t[0][0]==0){
b.dropPiece(new PieceLocation(-1,0,0));return true;
}else if(t[0][2]==t[1][1]&&t[0][2]==f&&t[2][0]==0){
b.dropPiece(new PieceLocation(-1,2,0));return true;
}else if (t[1][1]==t[2][0]&&t[1][1]==f&&t[0][2]==0){
b.dropPiece(new PieceLocation(-1,0,2));return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}//包含任何己方两枚棋子连接在一起,且连线有空位的情况
//(横向、纵向和斜着的方向)
public boolean center(){
if(t[1][1]==0){
b.dropPiece(new PieceLocation(-1,1,1));return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
public void planB(){
if(t[0][0]==t[2][2]&&t[0][0]==1||t[0][2]==t[2][0]&&t[0][2]==1){
if(t[0][2]==0){
b.dropPiece(new PieceLocation(-1,0,2));
}else{
b.dropPiece(new PieceLocation(-1,0,0));
}//特殊情况实现代码
}else if((t[0][1]==1||t[1][2]==1)&&t[2][0]==0){
b.dropPiece(new PieceLocation(-1,2,0));
}else if((t[1][0]==1||t[2][1]==1)&&t[0][2]==0){
b.dropPiece(new PieceLocation(-1,0,2));
//以上四行为先角原则的实现 以下为垃圾时间代码实现,即从座至右,
//从上到下,扫描整个棋盘,然后寻找空位,落子。
}else if(t[0][0]==0){
b.dropPiece(new PieceLocation(-1,0,0));
}else if (t[0][2]==0){
b.dropPiece(new PieceLocation(-1,0,2));
}else if(t[2][0]==0){
b.dropPiece(new PieceLocation(-1,2,0));
}else if (t[2][2]==0){
b.dropPiece(new PieceLocation(-1,2,2));
}else if(t[0][1]==0){
b.dropPiece(new PieceLocation(-1,0,1));
}else if(t[1][0]==0){
b.dropPiece(new PieceLocation(-1,1,0));
}else if(t[1][2]==0){
b.dropPiece(new PieceLocation(-1,1,2));
}else
b.dropPiece(new PieceLocation(-1,2,1));
}
}
The Original Link: http://baham.github.io/08_02_328.html
If you want to reprint it, please do under the CC BY-NC-SA 4.0